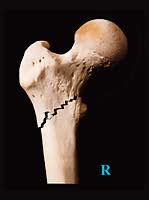
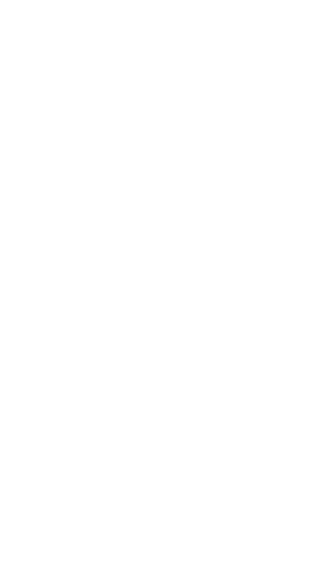Trauma mechanisme
Meestal door val op heup zelf
Pijn in de heupstreek.
Been ligt in exorotatie
Been is bij dislocatie verkort
– Bij pijn: 10 mg morfine i.m. pijnstilling
– Decubituspreventie!
– Xft.: Bekken + axiale foto heup
Volgens lokaal ziekenhuisprotocol
– Antibioticaprofylaxe:
– Postop thromboseprofylaxe
Indeling
1. Pertrochantere fracturen
Alle fracturen tussen bovenkant trochanter major naar trochanter minor én onderkant trochanter major naar trochanter minor
2. Intertrochantere fractuur
Laterale collum fractuur (heeft biologisch zelfde gedrag als 1)
3. Diatrochantere fractuur
Vrij dwars van onder trochanter major naar bovenzijde trochanter minor
4. “Reversed fracture”
Omgekeerde fractuurrichting (Evans V)
5. Subtrochantere fracturen
Proximaal in het femur nét onder ’ t trochanter massief
N.B.:
– Is er osteoporose
– Is er artrose
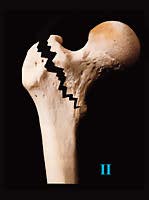
Figure 1 Evans’ classification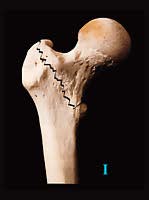 Type I: Undisplaced 2-fragment fracture | |
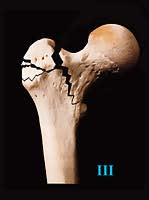 Type III: 3-fragment fracture without posterolateral support, owing to displacement of greater trochanter fragment |
|
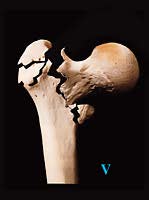 Type V: 4-fragment fracture without posterolateral and medial support (combination of Type III and Type IV) | |
Pertrochantere fracturen
Beoordeel stabiliteit a.d.h.v. Röntgenfoto
– stabiel (± 70%) Evans I en II
calcar femorale en trochanter Minor is intact
– instabiel (± 30%) Evans III, IV en V
veel osteoporose
Behandeling Conservatief
Zweefrekverband ( in Nederland zelden)
Direct belast lopen is met beide methoden mogelijk
Subtrochantere femurfractuur
Behandeling Operatief
Meestal intramedulaire pen (verlengde) gamma nail of PFN 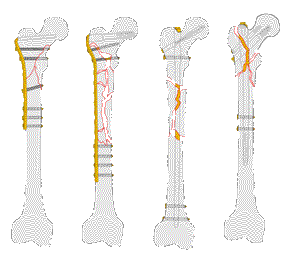
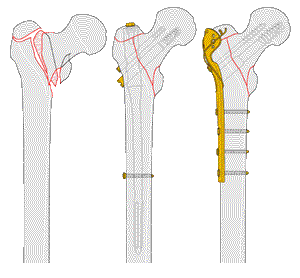
Evt. DCS (Dynamische Condylen Schroef) of DHS evt. 95° hoekplaat